Source: North Dakota State University Extension
Corky ring spot is becoming more economically important across several potato production regions in the U.S. largely due to the spread of the virus and because of restrictions on the use of current chemical control options.
Tobacco rattle virus incidence has been reported in potato production areas in California, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Michigan, Minnesota, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington and Wisconsin. The virus has a broad host range, including potato, tobacco, corn, barley, sunflower, ornamental (tulip, iris, etc.) and a variety of weed hosts. The virus is transmitted in the field by soil-inhabiting stubby root nematodes of the genera Trichodorus and Paratrichodorus.
Nematicides, soil fumigation and resistant cultivars can be used for nematode management. Detecting and quantifying viruliferous nematodes is important for making planting decisions and management approaches.
Symptoms
Internal TRV-induced symptoms often are confused with tuber necrosis symptoms caused by the potato mop-top virus (see NDSU Extension publication “Potato Tuber Viruses: Mop-top Management,” A1777). Tuber necrosis symptoms caused by TRV appear as rust/brown arcs, concentric rings or extensive browning of tuber tissue that later dry into corklike tissue (Figure 1). Concentric rings or arcs also may appear externally on tuber skin (Figure 2) and are very similar in appearance to symptoms caused by potato virus Y (PVYntn).



Figure 1. Characteristic TRV symptoms in potato. (S.K.R. Yellareddygari, NDSU)


Figure 2. External arclike symptom appearance on tuber skin. These symptoms are similar to symptoms produced by the strains of PVYntn. (S.K.R. Yellareddygari, NDSU)
Important note: The necrosis symptoms in some cultivars increase during the time that potatoes are in storage. Symptom intensity varies from cultivar to cultivar (Figure 3), field to field, location to location and year to year. Laboratory analysis is the best method to determine the specific virus.
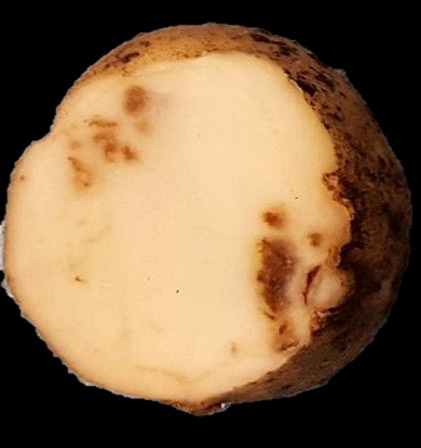


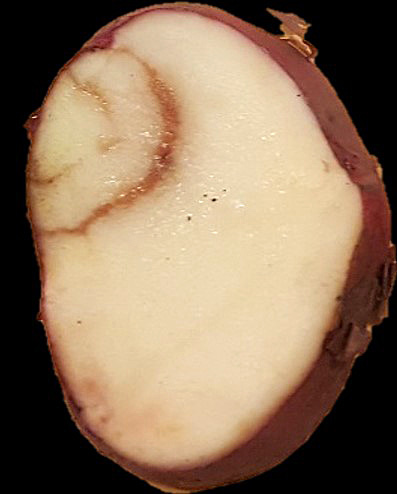
Figure 3. Varying TRV-induced necrosis in potato cultivars. Top to bottom: Russet, specialty and red market type cultivars. (S.K.R. Yellareddygari, NDSU)
Disease Development
Stubby root nematodes are obligate parasites, meaning they have to feed on host plants to survive. The life cycle of stubby root nematodes is short and ranges from 16 to 20 days.
Females lay eggs and juveniles undergo four molts to reach adult stages. All stages (juveniles and adult) of nematodes feed and destruct the plant root cells by feeding on tissues while remaining outside of the plant. Adult and juvenile stages of nematode can transmit TRV when feeding on a plant root or tuber.
Tobacco rattle virus is acquired by nematodes while feeding on diseased plant tissue of potato or reservoir weed hosts. Within a field, CRS is spread when viruliferous nematodes move from diseased to healthy plants. The virus is lost during juvenile nematode molting and the nematodes reacquire the virus when feeding on roots of infected plants.
Stubby root nematodes prefer sandy, moist, cool soils and are highly sensitive to soil moisture and temperature. Tobacco rattle virus is introduced into new regions through movement of vector-infested soil and/or by planting infected seed material.
Testing for the presence of vector nematodes prior to planting is important to assist growers in making planting decisions. Soil samples can be collected throughout the year if the soil is not too dry, wet or frozen.
Collect samples at a soil depth of 12 to 18 inches and submit them for nematode detection. Based on the soil results, growers may consider implementing nematode management strategies.
Tobacco Rattle Virus Management
Here are some strategies for reducing the risk of the tobacco rattle virus:
- Abandon fields highly infested with TRV. This is one of the best management options.
- Avoid planting TRV-sensitive cultivars (see Table 1).
- Use virus-free seed. It is the most effective strategy for managing TRV. Planting clean seed is important because TRV can survive in infected seed tubers and spreads from one season to the next.
- Practice crop rotation using TRV non-host crop alfalfa Control weeds to lower the viruliferous stubby root nematode numbers. Common weeds such as chickweed, nightshade and purslane can act as hosts for TRV, and proper weed control greatly reduces CRS disease.
Stubby root nematode mobility (horizontal and vertical direction) in the soil makes nematode management difficult. No chemical completely controls the vector. Application of 1,3 dichloropropene (Telone™)-based products provide partial control of vector nematodes. Oxamyl-based products applied at planting and post-emergence also provide some control of the nematode vectors.